Understanding MSMEs To Help Them Succeed And Grow
Risks and Challenges Behind Failure Rates
MSMEs are pivotal to global economies, representing approximately 90% of businesses and contributing significantly to employment and GDP, particularly in emerging markets. However, these enterprises face substantial challenges, especially within their initial years, leading to notable failure rates.
Global Failure Rates in the First Five Years
Failure rates among MSMEs during their first five years vary across regions and industries. In the United Kingdom, for instance, more than half of SMEs fail within this period, often due to poor financial management and administrative challenges. In the United States, data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics indicates that approximately 20% of startups do not survive their first year, and only about one-third remain after ten years. While comprehensive global statistics are limited, these figures underscore the vulnerability of MSMEs worldwide during their formative years.
Particular Risks During this Period
Understanding the reasons behind the failure is crucial for developing strategies to enhance their survival and success. Based on various studies, the primary causes of failures globally, along with their approximate percentages, are as follows:
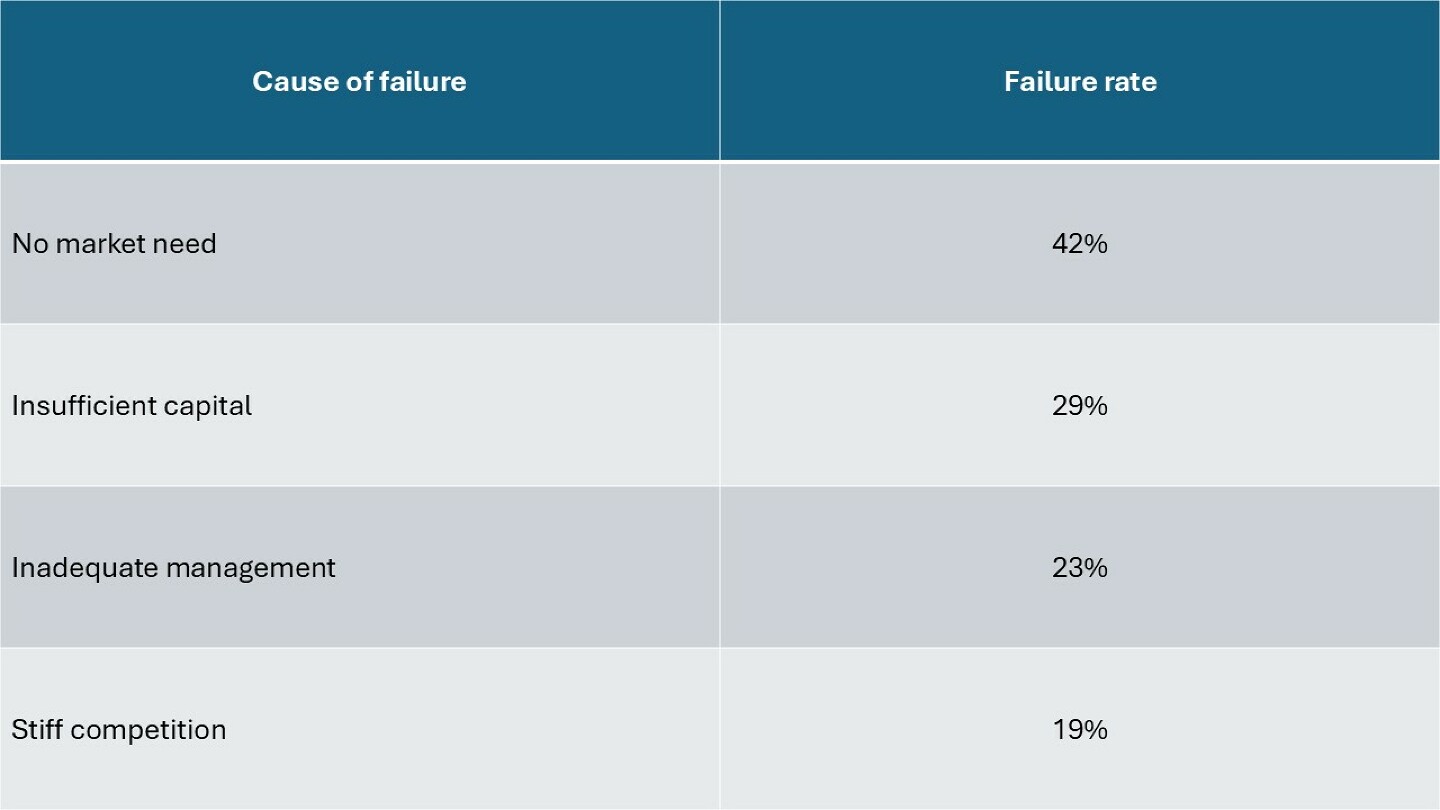
These percentages provide a general overview and may vary across different regions and industries. Addressing these challenges requires targeted interventions, such as conducting thorough market research, ensuring adequate capitalisation, enhancing managerial skills, differentiating from competitors, implementing effective pricing strategies, navigating regulatory environments, and executing well-planned marketing campaigns.
Impact of Failures
The closure of businesses has significant socio-economic repercussions, leading to job losses, diminished economic activity, and heightened poverty levels. While specific studies quantifying the exact number of direct and indirect job losses per MSME closure are limited, several sources highlight the broader impacts on employment and local economies:
- Local employment impact: MSMEs are crucial employment providers, especially in emerging markets, accounting for approximately 45% to 50% of total employment. Their closure can lead to substantial job losses, contributing to increased unemployment rates; (Source: McKinsey)
- Local economic effects: The shutdown of MSMEs can lead to reduced foot traffic, making it harder for remaining businesses to thrive. This decline in activity affects employment opportunities and consumer spending, further straining the local economy; (Source: Adcroft Hilton)
- Community well-being: Beyond economics, the loss of MSMEs can erode social cohesion, as these businesses often serve as community hubs, providing essential services and maintaining community engagement. (Source: Small Business Connections)
While a specific study quantifying the loss of multiple direct and indirect jobs per MSME closure is not readily identified, the cumulative effect of MSME failures underscores the need for targeted support and intervention to mitigate these adverse outcomes.
Stakeholders Addressing Challenges
To address the challenges faced by MSMEs, a collaborative effort from various stakeholders is essential. Each of these entities plays a critical role in supporting them, ensuring they have the resources, knowledge, and infrastructure to overcome obstacles, scale, and thrive. Here's a deeper look at the stakeholders involved in helping them succeed, with an emphasis on the role of governments and banks.
Governments: A Key Enabler of MSME Growth
Governments are foundational in encouraging an environment that supports MSME development. Their policies and actions shape the economic landscape in which these businesses operate. Several key areas where governments make a substantial impact include:
- 1. Regulatory framework and financial incentives: Governments can create an enabling environment by implementing business-friendly policies, reducing red tape, and ensuring that regulations are simplified and accessible. Tax incentives, subsidies, and financial grants can help MSMEs reduce their financial burden, especially in the early stages of their lifecycle. For example, offering tax breaks or low-interest loans for businesses focused on innovation or sustainable practices helps them grow without excessive financial pressure;
- 2. Business development services: Governments can invest in programs designed to educate and mentor business owners, especially new entrepreneurs. Through business development services, such as skills training, workshops, and mentorship programs, governments provide MSMEs with the tools to enhance their operational knowledge and improve their competitiveness;
- 3. Financial support mechanisms: Governments can also set up funding schemes, loan guarantee programs, and specialist development banks to support MSMEs, particularly those that struggle to access credit from commercial banks due to lack of collateral or credit history. These mechanisms help reduce financing gaps by offering affordable loans, micro-financing, and credit guarantees;
- 4. Infrastructure and market access: By investing in infrastructure such as transportation networks, digital connectivity, and utilities, governments create a foundation for MSMEs to expand and operate more efficiently. Additionally, governments can promote MSME participation in public procurement, creating a direct channel for small businesses to access larger contracts and new markets.
Banks and Financial Institutions: Essential Partners
Banks and financial institutions are pivotal in providing the necessary financial services that enable MSMEs to function and grow. They are integral in offering access to capital, managing finances, and mitigating financial risks. Their role can be broken down into the following areas:
- 1. Tailored financial solutions: MSMEs often require different types of financial products compared to larger enterprises. Banks can offer specialised services such as working capital loans, asset financing, and trade finance that cater specifically to the cash flow challenges and operational needs of MSMEs. These solutions are designed to support day-to-day operations, fund expansions, and address short-term liquidity needs;
- 2. Digital banking and fintech solutions: Digital banking tools are increasingly important for MSMEs to streamline operations. Banks can offer online banking services, mobile payment systems, and e-commerce solutions that make financial management more efficient and accessible. These digital platforms not only simplify cash flow management but also allow them to engage with customers and suppliers more effectively. Additionally, financial institutions can provide tools for inventory management, invoicing, and payroll systems, helping businesses run smoothly;
- 3. Advisory services and risk management: Beyond providing capital, banks can help MSMEs by offering advisory services, particularly in financial planning, risk management, and strategic decision-making. By educating MSME owners on how to manage cash flow, handle debt responsibly, and mitigate risks, banks can help them make more informed business decisions. Furthermore, banks can assist them in managing financial uncertainties by offering risk management products such as insurance or hedging services;
- 4. Access to additional funding sources: Banks can play an important role in connecting MSMEs to other funding opportunities, including venture capitalists, private equity firms, and government funding programs. By fostering networks and partnerships, financial institutions can expand the pool of resources available to them, helping them scale operations and achieve sustainable growth.
Other Stakeholders
In addition to governments and banks, several other stakeholders provide essential services and support to MSMEs:
- Investors and venture capitalists: Investors, including venture capitalists and angel investors, play a critical role in supporting high-growth potential MSMEs. They provide not only funding but also strategic guidance, helping businesses scale and innovate. They are particularly crucial for businesses in the growth phase, offering capital that banks may not be willing to provide due to the higher risk involved;
- Industry associations and Chambers of Commerce: These organisations advocate for the interests of MSMEs and provide networking opportunities, training, and market insights. By acting as intermediaries between businesses and policymakers, they help ensure that the needs and challenges of MSMEs are considered in policy formulation;
- Educational Institutions and Business Consultants: Universities, training centres, and business consultants offer vital business education and mentorship to MSME owners. Their services include leadership development, financial literacy, market research, and business strategy, which are all essential for helping businesses enhance their capabilities and stay competitive;
- Technology providers: MSMEs benefit greatly from innovations provided by technology providers. Digital tools and platforms, ranging from accounting software to CRM systems, help them streamline operations, improve customer service, and increase efficiency. Technology providers also offer e-commerce platforms, which help them expand their market reach and engage with customers globally;
- Non-government organisations and development agencies: NGOs and development agencies often focus on providing financial support, market access, and business development programs, particularly in underserved or marginalised regions. These organisations can offer grants, loans, and capacity-building programs that help them enter new markets or implement sustainable practices.
Building a Strong Ecosystem for MSME Success
A strong MSME ecosystem requires collaboration among governments, banks, investors, industry associations, and educational institutions. Governments provide policy support and infrastructure, while banks offer financial products, digital solutions, and advisory services. With the right support, MSMEs can thrive, driving economic growth and job creation.
